Informationen på denna sida är på engelska.
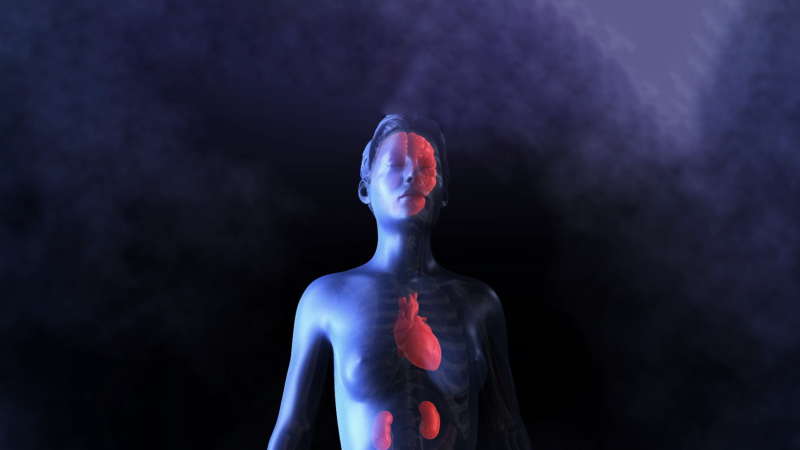
The clinical presentation of cTTP ranges from life-threatening, acute, overt TTP events to milder TTP manifestations, including thrombocytopenia, haemolytic anaemia, abdominal pain, headaches and neurological symptoms. End-organ damage due to recurrent overt and nonovert TTP, such as stroke, chronic kidney disease, or cardiac involvement, can also develop. 1 1. Scully M, et al. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(17):1584-1596.
Although first symptom occurrence of cTTP has classically been described in childhood, presentation can occur at any age, with a notable peak in women during pregnancy. 2 2. Alwan F, et al. Blood. 2019;133(15):1644–1651.
A review of cTTP cases found that genetic mutations differed by age of onset with prespacer mutations more likely to be associated with childhood onset. In this review, pregnancy was the most common trigger of adult-onset cTTP, accounting for 69% of adult presentations. 2 2. Alwan F, et al. Blood. 2019;133(15):1644–1651.

Diagnosis of TTP is challenging because of its diverse clinical manifestations, overlap in clinical presentation with other thrombotic microangiopathies, and limited availability of ADAMTS13 testing. 4 4. Chiasakul T et al. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2018;2018(1):530–538. As a result, cTTP may be undiagnosed in many patients. 6 6. Matsumoto M, et al. Int J Hematol. 2023;118(5):529-546.
The ultra-rarity of cTTP and its variable phenotype may often delay the correct diagnosis.
5
5. Ferrari B, et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2019;17(4):666-669.
Diagnosis of TTP may be challenging too, due to the limited availability of ADAMTS13 testing.
4
4. Chiasakul T et al. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2018;2018(1):530–538.
A high index of suspicion should be kept in mind for all patients presenting with an acute thrombotic microangiopathy, regardless of age.
5
5. Ferrari B, et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2019;17(4):666-669.
Tests, such as ADAMTS13 activity assays, can then help to confirm TTP diagnoses.
1
1. Scully M, et al. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(17):1584-1596.
5
5. Ferrari B, et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2019;17(4):666-669.
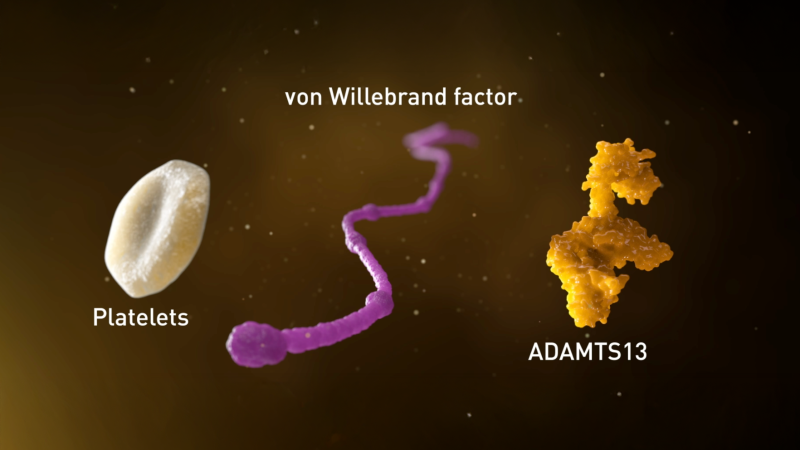
Among patients with severe thrombocytopenia and haemolytic anaemia of unknown cause, the reduction in ADAMTS13 levels to <10% of normal values confirms a diagnosis of TTP.
1
1. Scully M, et al. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(17):1584-1596.
3
3. Sakai K et al. J Clin Med. 2023;12(10):3365.
A diagnosis of cTTP is then confirmed through genetic analysis and identification of causative ADAMTS13 mutations. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) direct sequencing, can be used to analyse the patient’s genes to detect ADAMTS13 mutations.
3
3. Sakai K et al. J Clin Med. 2023;12(10):3365.
Increased education of cTTP and wider availability of ADAMTS13 assays could lead to more accurate and timely diagnoses.
2
2. Alwan F, et al. Blood. 2019;133(15):1644–1651.
When coupled with earlier treatments, greater understanding and clarity of cTTP could lead to better patient outcomes.
2
2. Alwan F, et al. Blood. 2019;133(15):1644–1651.
Acronyms
ADAMTS13, A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with a thrombospondin motifs 13
cTTP, Congenital TTP
PCR, Polymerase chain reaction
SmPC, Summary of product characteristics
TTP, Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura